03-解析全局配置文件
| 版本 | 内容 | 时间 |
|---|---|---|
| V1 | 新建 | 2021年6月7日00:21:08 |
摘要:本篇主要讲解Mybatis的全局配置文件时如何解析的,在解析完配置文件后会得到一个默认的SqlSession工厂SqlSessionFactory对象。
在入门案例中我们得到SqlSession对象去调用它的API去完成数据库的操作,而SqlSession对象的创建时比较复杂的。
SqlSession及相关的类组成了一个链,先是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder生成SqlSessionFactory,然后SqlSessionFactory生成SqlSession。
那我们首先看SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类。
// 1. 读取核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
// 2. 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder构造者对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 3. 使用构造者builder,根据配置文件的信息is,构造一个SqlSessionFactory工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(is);
// 4. 使用工厂对象factory,生产一个SqlSession对象
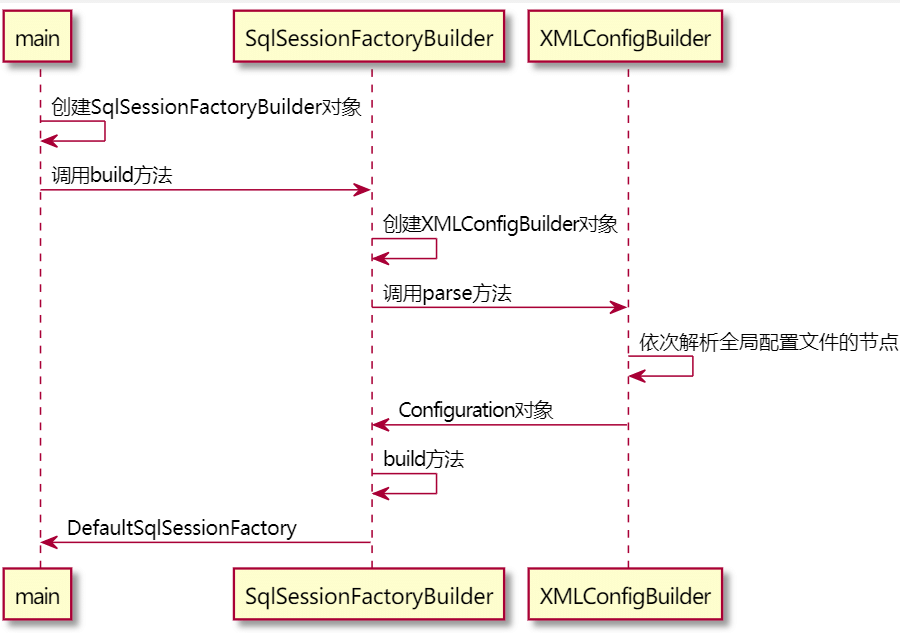
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();先看下解析全局配置文件的时序图,有个印象,本篇看完后回过头来再看就有收获了。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类是SqlSessionFactory类的建造者类,里面有很多重载的build方法,都是用来创建SqlSessionFactory对象的,里面有两个核心的build方法,但是这两个方法代码基本相同,拿一个出来如下
/**
* 建造一个SqlSessionFactory对象
*
* @param reader 读取字符流的抽象类
* @param environment 环境信息
* @param properties 配置信息
* @return SqlSessionFactory对象
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// 根据传入的配置文件,创建一个XMLConfigBuilder类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
// 首先XMLConfigBuilder解析配置文件,得到配置文件对应的Configuration对象
// 根据Configuration对象,调用build方法,获得一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}上面解析得到Configuration对象对象后,会调用一个build方法得到一个默认的DefaultSqlSessionFactory,如下:
/**
* 根据配置信息建造一个SqlSessionFactory对象
*
* @param config 配置信息
* @return SqlSessionFactory对象 总是DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}小结:
SqlSessionFactory对象的创建主要有以下步骤:
- 首先根据传入的配置文件,创建一个XMLConfigBuilder类,为后续的配置文件的解析做准备。
- 调用XMLConfigBuilder对象的parse()方法对配置文件进行解析,得到一个Configuration对象。
- 调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法,传入解析好的Configuration得到一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
创建XMLConfigBuilder
在讲解XMLConfigBuilder类之前,先简单分析下整个Builder的结构。
虽然BaseBuilder类是抽象类,但是BaseBuilder类中并没有抽象方法。它的各个子类的功能都不同,例如本篇要分析的XMLConfigBuilder就是用来解析全局配置文件的,而XMLMapperBuilder是用来解析Mapper映射文件的,等等。
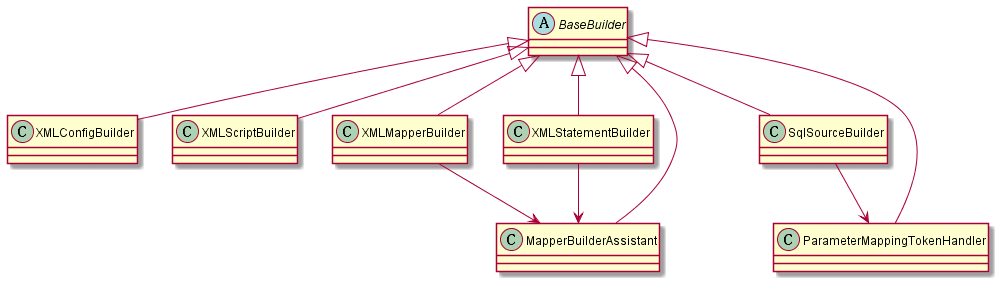
XMLConfigBuilder类继承自BaseBuilder基类,从XMLConfigBuilder类的名字就可以看出它时候用来解析配置文件的。
XMLConfigBuilder的字段如下:
// 存储是否已经对config文件完成解析
private boolean parsed;
// 解析器
private final XPathParser parser;
// 要读取哪一个Environment节点,这里存储节点名
private String environment;
// 反射工厂
private final ReflectorFactory localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();还有继承BaseBuilder的一些字段
// 全局配置类
protected final Configuration configuration;
// 类型别名注册表
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry;
// 类型处理器注册表
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;在SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类中调用了下面的方法来创建XMLConfigBuilder对象。
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);依次会调用下面两个构造方法:
public XMLConfigBuilder(Reader reader, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration()); // 调用父类的构造方法赋值
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props); // 设置参数
this.parsed = false; // parsed对象表示是否已经对配置文件解析过
this.environment = environment; // 环境相关
this.parser = parser;
}这样XMLConfigBuilder就创建成功了,先不用管其它字段有什么用,先混个眼熟,主流程为主。
XMLConfigBuilder的parse方法
在得到XMLConfigBuilder对象后,直接调用其它的parse()方法去解析配置文件。
XMLConfigBuilder的parsed字段是为了防止Mybatis重复解析配置文件。
/**
* 解析配置文件的入口方法
*
* @return Configuration对象
*/
public Configuration parse() {
// 不允许重复解析
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
// 标志已经解析过配置文件
parsed = true;
// 从根节点开展解析
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}解析配置文件的重点来了,就是上面的parseConfiguration(XNode)方法。Myabtis规定配置文件的根标签是<configuration>,所以上面的parser.evalNode("/configuration"),表示从根节点开始解析。
在看下parseConfiguration(XNode)方法之前,我们看下Mybatis的配置文件能够配置那些东西,就是根节点<configuration>下面有那些允许的子节点:
Mybatis的配置文件的结构如下:
configuration(配置)
properties(属性)
settings(设置)
typeAliases(类型别名)
typeHandlers(类型处理器)
objectFactory(对象工厂)
plugins(插件)
environments(环境配置)
environment(环境变量)
transactionManager(事务管理器)
dataSource(数据源)
databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识)
mappers(映射器)看了Myabtis配置文件的结构之后再看parseConfiguration(XNode)方法就很明了了,就是挨个节点去解析而已。
/**
* 从根节点configuration开始解析下层节点
*
* @param root 根节点configuration节点
*/
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
// 解析信息放入Configuration
// 首先解析properties,以保证在解析其他节点时便可以生效
// issue #117 read properties first
// 解析properties属性
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析setting
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
// 解析我们配置指定的 VFS 的实现
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
// 解析类型别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析插件
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析对象工厂
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
// 设置上面解析出来的settings的信息到configuration中
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析环境
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析数据库厂商标识
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析类型处理器
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析映射器
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}上面这么多解析节点的方法,拿出几个来讲
- 解析properties节点。
- 解析setting节点。
- 解析mapper节点。(本篇不介绍,内容很多,后面再分析)
解析properties节点
首先看下 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));,这个主要是用来解析properties节点的信息。
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 获得配置的Properties属性
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
// 只允许resource和url同时存在一个
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
if (resource != null) {
// 读取resource配置的Properties属性,假如同名的话就会覆盖
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
// 读取url配置的Properties属性,假如同名的话就会覆盖
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}从上面的源码可以很容易看到,如果一个属性在不只一个地方进行了配置,那么,MyBatis 将按照下面的顺序来加载:
- 首先读取在 properties 元素体内指定的属性。
- 然后根据 properties 元素中的 resource 属性读取类路径下属性文件,或根据 url 属性指定的路径读取属性文件,并覆盖之前读取过的同名属性。
- 最后读取作为方法参数传递的属性,并覆盖之前读取过的同名属性。
因此,通过方法参数传递的属性具有最高优先级,resource/url 属性中指定的配置文件次之,最低优先级的则是 properties 元素中指定的属性。
需要注意的是,把解析properties属性放在首位的原因是,先解析properties属性可以方便后续解析其他节点的时候这些properties属性可以被使用。
解析setting节点
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) {
if (context == null) {
return new Properties();
}
// 读取setting的子节点的信息为Properties
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
// 下面的操作就是为了检查setting中的配置是否存在
// 就是判断Configuration类中是否有对应的setter方法
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory);
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
// 大小写敏感
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
return props;
}关于解析setting节点需要注意的是,我们必须把我们要设置的属性名字写对,不能瞎写,瞎写Mybatis不认识也是白搭,会直接报错。
Mybatis中有个核心配置类Configuration类,里面有很多属性可以配置,判断配置文件中的setting标签的属性是否写对就是判断Configuration类中是否有对应的setter方法而已。
在解析setting得到一个Properties之后,会调用settingsElement(settings);方法设置到configuration属性中,当遇到没有setting标签没有配置时,会给出一个默认值。
给出部分代码上来:
private void settingsElement(Properties props) {
// 省略部分...
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
// 省略部分...
}其他配置解析
最后的解析mapper节点的内容比较多,本篇不介绍,后续再说。
关于其他配置,大家自己去看,都是很简单的操作,最后将解析出来的信息设置到Configuration全局配置类中。
获取SqlSessionFactory工厂
在得到Configuration对象后,调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法得到默认的DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
/**
* 根据配置信息建造一个SqlSessionFactory对象
*
* @param config 配置信息
* @return SqlSessionFactory对象 总是DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}好了,此处讲到解析配置文件得到SqlSessionFactory工厂,那么Mybatis的配置文件到这里基本讲了个大概。
小结
总结一下是如何得到DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象的。
- 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder建造者对象。
- 调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法
- 在SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法内,会创建专门用于解析去全局配置文件的XMLConfigBuilder对象。
- 创建好XMLConfigBuilder对象后,会调用该对象的parse方法挨个解析全局配置文件的节点,最终都会把解析的信息设置到全局配置类Configuration中。
- 在得到Configuration的对象后,调用build的一个重载方法后,得到一个默认的DefaultSqlSessionFactory工厂对象。