05-线程体系-NioEventLoop相关接口分析
| 版本 | 内容 | 时间 |
|---|---|---|
| V1 | EventExecutorGroup | 2022年1月27日11:38:16 |
| V2 | 新增相关接口 | 2022年1月27日12:29:06 |
| V3 | 重构 | 2023年05月16日00:12:52 |
NioEventLoop 继承体系
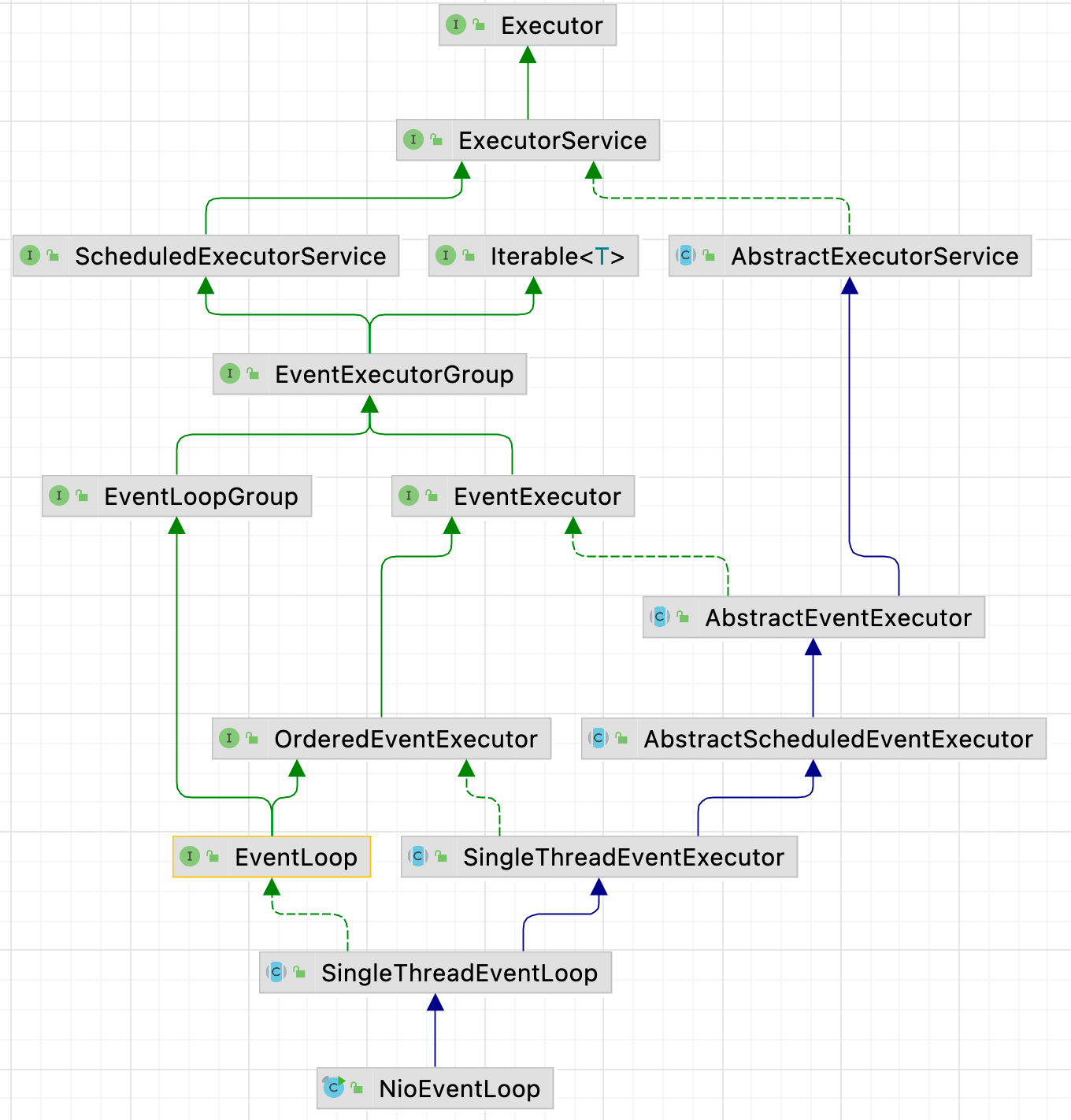
NioEventLoop 父接口
NioEventLoop 的继承体系中,它的父接口如下:
- java.util.concurrent.Executor:JDK 提供的执行器的顶级接口;
- java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService:继承 Executor 接口,额外提供了一些线程池生命周期的方法;
- java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService:JDK 的调度线程池的接口,提供了一些周期、延迟的 API;
- java.lang.Iterable:JDK 的迭代接口;
- io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup:Netty 的接口,主要提供了一个 next 方法,用于获取池中的某个执行器;
- io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup:主要提供了 Channel 绑定执行器的 register 方法;
- io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutor:主要提供一个 inEventLoop 方法,用于判断当前执行线程是不是指定的线程;
- io.netty.util.concurrent.OrderedEventExecutor:仅仅是一个标记接口;
- io.netty.channel.EventLoop:提供方法,返回当前 EventLoop 实例是属于那个 EventLoopGroup 管理的;
EventExecutorGroup 接口
概要
继承体系:
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, Iterable<EventExecutor> {
}该接口主要提供了下面的 API:
- EventExecutorGroup 通过 next 方法提供 EventExecutor 实例;
- 除此之外,EventExecutorGroup 还负责处理它们的生命周期并允许以全局方式关闭它们;
- EventExecutorGroup 中重写了 ScheduledExecutorService 接口中的一些方法,修改了方法的返回值;
接口源码
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, Iterable<EventExecutor> {
/**
* 当且仅当该 EventExecutorGroup 管理的所有 EventExecutor
* 都使用 `shutdownGracefully()` 或者 `isShutdown()` 关闭时 才返回true。
*/
boolean isShuttingDown();
/**
* 优雅地关闭 EventExecutorGroup
* 使用默认值调用 shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit) 方法
* 返回值就是 terminationFuture() 方法返回值
*/
Future<?> shutdownGracefully();
/**
* 向此执行程序发出信号,表明调用者希望关闭执行程序。
* 一旦调用此方法, isShuttingDown()开始返回true ,并且执行程序准备关闭自己。
* 与shutdown()不同,优雅关机确保在它自己关闭之前,在“安静期” (通常是几秒钟)内不会提交任何任务。
* 如果在静默期提交任务,则保证被接受,静默期将重新开始
*/
Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* 当该 EventExecutorGroup 管理的所有 EventExecutor 被终止时,该Future会被通知。
*/
Future<?> terminationFuture();
/**
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
void shutdown();
/**
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
/**
* 返回该 EventExecutorGroup 所管理的一个 EventExecutor 实例
*/
EventExecutor next();
@Override
Iterator<EventExecutor> iterator();
@Override
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
@Override
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
@Override
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
}扩展的方法
(1)shutdownGracefully 关闭系列方法。
Future<?> shutdownGracefully();Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
在 ScheduledExecutorService 接口中本来也有关闭执行器的 shutdown 和 shutdownNow 方法。shutdownGracefully 方法和它们的区别是在执行器关闭这段时间内,假如有任务添加,它也保证任务被接收。
(2)isShuttingDown 方法
表示 EventExecutorGroup 中的所有的执行器 EventExecutor 正在进行关闭,也就是调用了 shutdown 系列方法。
(3)terminationFuture方法
当 EventExecutorGroup 中所有的执行器 EventExecutor 都被关闭时会返回一个 Future 通知。
(4)next 方法
EventExecutorGroup 中管理多个执行器 EventExecutor,next 方法的作用是返回一个执行器对象。
重写的方法
在 EventExecutorGroup 接口中重写了一些提交任务的方法。主要是将方法的返回值由 JDK 的(Future 和 ScheduledFuture)对象改为了 Netty 自己的(Future 和 ScheduledFuture)对象。如下:
@Override
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);EventLoopGroup 接口
EventLoopGroup 接口主要提供了 Channel 绑定执行器的 register 方法。这样事件执行器就可以处理通道 Channel 的 I/O 操作,也就变成了事件轮询器 EventLoop。
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* 返回下一个 EventLoop
* 复写了 EventExecutorGroup 的方法,改变了返回值类型
*/
@Override
EventLoop next();
/**
* 向这个EventLoop注册一个Channel,一旦注册完成,返回的 ChannelFuture 将得到通知。
*/
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
/**
* 使用参数 ChannelPromise 向 EventLoop 注册一个Channel。
* (ChannelPromise类中包含一个Channel)
* 一旦注册完成,传递的 ChannelPromise 将得到通知,返回的 ChannelFuture 也将得到通知。
*/
ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise);
@Deprecated
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise);
}EventExecutor 接口
EventExecutor 接口主要提供了 inEventLoop 方法,用于判断当前执行代码的线程是否是指定线程。
public interface EventExecutor extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* 返回自己
*/
@Override
EventExecutor next();
/**
* 返回管理该事件执行器EventExecutor的父EventExecutorGroup
*/
EventExecutorGroup parent();
/**
* 相当于 inEventLoop(Thread.currentThread())
*/
boolean inEventLoop();
/**
* 如果给定的Thread在事件循环中执行,则返回true否则返回false 。
*/
boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread);
/**
* 返回一个新的 Promise 实例
*/
<V> Promise<V> newPromise();
/**
* 返回一个新的 ProgressivePromise 实例
*/
<V> ProgressivePromise<V> newProgressivePromise();
/**
* 创建一个新的已经标记为成功的 Future,所以Future.isSuccess()将返回true 。
* 所有添加到它的FutureListener都会被直接通知。 此外,所有阻塞方法的调用都不会阻塞直接返回
*/
<V> Future<V> newSucceededFuture(V result);
/**
* 创建一个新的已标记为失败的Future,所以Future.isSuccess()将返回false 。
* 所有添加到它的FutureListener都会被直接通知。 此外,每次调用阻塞方法都会返回而不会阻塞
*/
<V> Future<V> newFailedFuture(Throwable cause);
}Q:EventExecutor 继承 EventExecutorGroup 接口,那么可能有疑问 EventExecutor 是不是也可以管理一些 EventExecutor 对象?
A:理论是是可行的,但是在一般情况下,在实现 EventExecutor 接口时,EventExecutor#next 返回的就是它自身。
EventLoop 接口
EventLoop 接口比较简单,主要就是提供了一个 parent 方法,该方法返回当前 EventLoop 实例是被那个 EventLoopGroup 管理的
public interface EventLoop extends OrderedEventExecutor, EventLoopGroup {
/**
* 返回管理该事件执行器EventLoop的父EventLoopGroup
*/
@Override
EventLoopGroup parent();
}